Your liver is one of the most vital and hardworking...
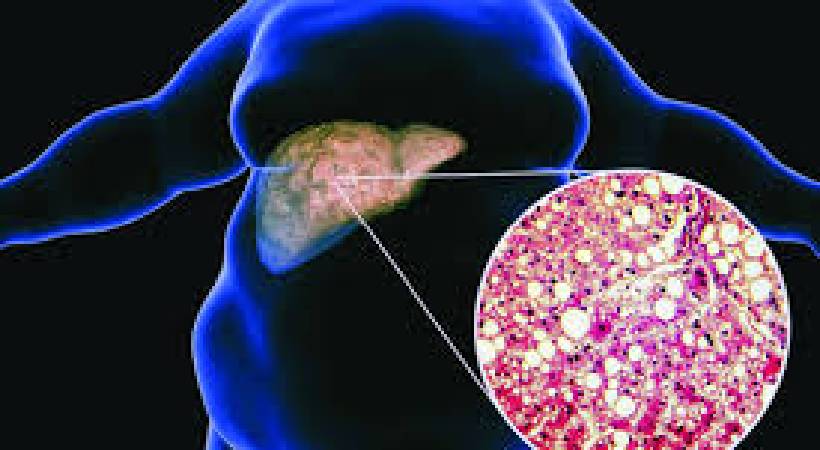
The liver, one of the largest organs in the human body, performs numerous vital functions, including metabolizing nutrients, detoxifying harmful substances, and producing essential proteins. Metabolic liver diseases encompass a group of disorders that disrupt these critical metabolic processes, leading to various health complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for metabolic liver diseases is essential for effective management and improved patient outcomes.
Causes of Metabolic Liver Diseases:
Metabolic liver diseases can arise from genetic mutations, environmental factors, or a combination of both. Some of the common causes include:
- Genetic Mutations: Inherited metabolic disorders such as Wilson’s disease, hemochromatosis, and alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can lead to liver dysfunction. These conditions are caused by mutations in genes responsible for metabolizing certain substances, resulting in their accumulation within the liver.
- Disorders of Carbohydrate, Fat, and Protein Metabolism: Conditions like glycogen storage diseases, fatty liver disease, and amino acid metabolism disorders can impair the liver’s ability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and proteins efficiently. This dysfunction often leads to the accumulation of toxic byproducts and lipid deposits within the liver cells.
- Alcohol and Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Excessive alcohol consumption and certain medications or toxins can cause liver damage by overloading its metabolic capacity or inducing inflammation. Chronic alcohol abuse, in particular, can lead to alcoholic liver disease, a prevalent form of metabolic liver disease worldwide.
Symptoms of Metabolic Liver Diseases:
The symptoms of metabolic liver diseases can vary widely depending on the specific disorder and its severity. However, some common signs and symptoms include:
- Fatigue and Weakness: Liver dysfunction can lead to a decrease in energy levels and overall fatigue due to impaired metabolism and nutrient processing.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, known as jaundice, can occur when the liver is unable to adequately process bilirubin, a waste product of red blood cell breakdown.
- Abdominal Pain and Swelling: Enlargement of the liver (hepatomegaly) and spleen (splenomegaly) may cause discomfort or pain in the upper right abdomen. Fluid accumulation in the abdomen (ascites) can also lead to abdominal swelling and discomfort.
- Easy Bruising and Bleeding: A dysfunctional liver may result in decreased production of clotting factors, leading to easy bruising and prolonged bleeding.
- Cognitive Impairment: In severe cases, metabolic liver diseases can cause cognitive impairment and hepatic encephalopathy, characterized by confusion, disorientation, and altered consciousness.
Treatment Options:
The treatment of metabolic liver diseases depends on the underlying cause and may involve a multidisciplinary approach including medical management, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes. Some common treatment options include:
- Medications: Depending on the specific disorder, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms, alleviate liver inflammation, or prevent complications such as cirrhosis and liver failure.
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a healthy diet low in fat, refined sugars, and alcohol can help reduce the burden on the liver and prevent further damage. In some cases, dietary supplements may be recommended to address specific nutritional deficiencies.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding alcohol, maintaining a healthy body weight, and engaging in regular physical activity are essential for preserving liver health and preventing disease progression.
- Liver Transplantation: In cases of advanced liver disease or liver failure, liver transplantation may be necessary to restore liver function and improve patient survival. Transplantation offers a potential cure for certain metabolic liver diseases, particularly those with significant liver damage.
Conclusion:
Metabolic liver diseases represent a diverse group of disorders that can significantly impact liver function and overall health. Early recognition, accurate diagnosis, and timely intervention are crucial for effectively managing these conditions and preventing complications. Through a combination of medical therapy, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes, individuals with metabolic liver diseases can lead healthier lives and reduce the risk of long-term complications. Ongoing research into the underlying mechanisms of these diseases and the development of novel treatment strategies offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals in the future.
Real Patients, Real Stories
Liver Transplant and Biliary Sciences Blogs
Understanding Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)
By Dr. Manoj Shrivastav — Liver Specialist, Pune The liver...
Liver Damage Due to Alcohol: Causes, Risks,
Alcohol consumption has become a common part of modern lifestyles....
Pune’s New Identity in Liver Transplantation :
यकृत प्रत्यारोपणातील पुण्याची नवी ओळख : डॉ. मनोज श्रीवास्तव यांचे...





