Your liver is one of the most vital and hardworking...
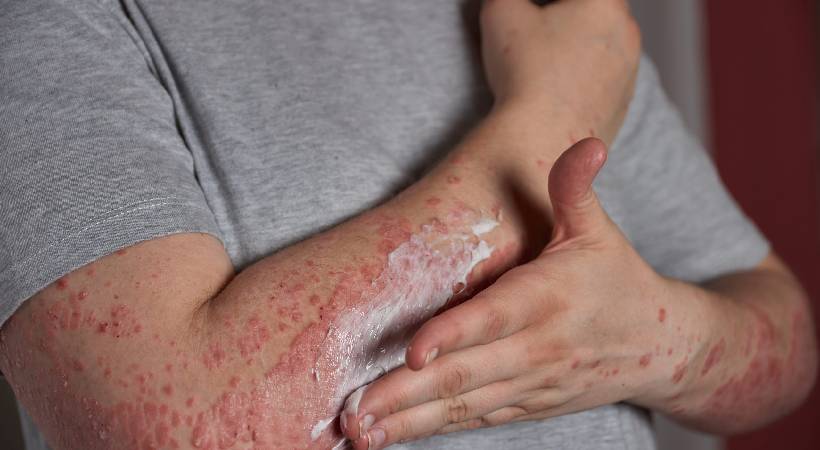
Autoimmune diseases are a group of disorders characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking the body’s own tissues. While the immune system’s primary role is to defend against foreign invaders such as bacteria and viruses, in autoimmune diseases, it becomes confused and launches an assault on healthy cells and tissues. This phenomenon leads to a wide range of conditions affecting various organs and systems in the body. Understanding autoimmune diseases is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals to effectively manage these complex conditions.
The Complexity of Autoimmune Diseases:
Autoimmune diseases encompass a vast array of conditions, each with its unique set of symptoms, triggers, and treatment approaches. Some of the most common autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and celiac disease. Despite their differences, these diseases share a common underlying mechanism: a malfunctioning immune system.
The immune system consists of a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs working together to protect the body. Normally, it can distinguish between self and non-self, attacking harmful invaders while leaving healthy cells untouched. In autoimmune diseases, this self-recognition mechanism fails, leading to the immune system mistakenly targeting the body’s own tissues.
Causes and Triggers:
The exact cause of autoimmune diseases remains elusive, but a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors is believed to play a role. Certain genetic variations predispose individuals to autoimmune conditions, making them more susceptible to developing these diseases. Environmental factors such as infections, exposure to toxins, and hormonal imbalances can also trigger autoimmune responses in genetically susceptible individuals.
Furthermore, emerging research suggests a link between autoimmune diseases and dysregulation of the gut microbiota, the community of microorganisms residing in the digestive tract. Disruptions in the balance of gut bacteria, often caused by factors like diet, antibiotics, and stress, may contribute to the development or exacerbation of autoimmune conditions.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Symptoms of autoimmune diseases can vary widely depending on the specific condition and the organs or systems affected. Common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, muscle weakness, skin rashes, gastrointestinal disturbances, and neurological problems. Because autoimmune diseases can mimic other conditions and present with vague symptoms, diagnosis can be challenging and often requires a thorough medical evaluation, including blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes biopsies.
Treatment and Management:
Treatment strategies for autoimmune diseases aim to alleviate symptoms, suppress immune activity, and prevent further damage to affected tissues. Depending on the severity and type of autoimmune disease, treatment may involve medications such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologic agents. Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, regular exercise, stress management techniques, and adequate sleep can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in alternative and complementary therapies for autoimmune diseases, including acupuncture, herbal supplements, and mind-body practices like yoga and meditation. While these approaches may offer symptom relief for some individuals, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating them into treatment plans.
The Road Ahead:
Despite significant advancements in research and treatment, autoimmune diseases remain a significant health challenge worldwide. As our understanding of the underlying mechanisms improves, so too will our ability to develop targeted therapies that address the root causes of these conditions. Additionally, efforts to raise awareness, promote early detection, and support patient advocacy are essential for improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals living with autoimmune diseases.
Conclusion:
Autoimmune diseases represent a complex and multifaceted group of disorders that pose challenges for both patients and healthcare providers. By unraveling the intricate interplay between genetics, environment, and immune dysregulation, we can gain insights into these conditions and develop more effective strategies for diagnosis, treatment, and management. With continued research and collaboration, we can strive towards better outcomes and improved quality of life for those affected by autoimmune diseases.
Real Patients, Real Stories
Liver Transplant and Biliary Sciences Blogs
Understanding Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)
By Dr. Manoj Shrivastav — Liver Specialist, Pune The liver...
Liver Damage Due to Alcohol: Causes, Risks,
Alcohol consumption has become a common part of modern lifestyles....
Pune’s New Identity in Liver Transplantation :
यकृत प्रत्यारोपणातील पुण्याची नवी ओळख : डॉ. मनोज श्रीवास्तव यांचे...





